ressonancia magnetica como é feito Como funciona a ressonância magnética?
When it comes to diagnostic imaging, two commonly used techniques are tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Both serve the purpose of capturing detailed images of the body’s internal structures, but they differ in terms of technology and indications.
Tomography: A Closer Look
Tomography, also known as computed tomography (CT), utilizes X-ray technology to create cross-sectional images of the body. It involves rotating X-ray machines that emit a series of narrow beams through the body from different angles.
These X-ray beams are captured by detectors and transformed into digital images by a computer. The images are then reconstructed to produce detailed slices or “tomograms” of the body part being examined.
Tomography is particularly useful in diagnosing conditions related to bones, such as fractures, tumors, and infections. It can also provide valuable insights into diseases affecting other areas of the body, including the chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A Different Approach

MRI, on the other hand, utilizes a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body’s soft tissues. Unlike tomography, MRI does not involve the use of ionizing radiation, making it a safer alternative in certain situations.
During an MRI scan, the patient lies down on a movable table, which slides into a large cylindrical machine. The magnetic field aligns the protons within the body’s tissues, and when radio waves are applied, these protons emit signals that are detected by the MRI machine.
The signals are then processed by a computer to create cross-sectional images of the body. MRI provides excellent clarity of soft tissues like muscles, tendons, brain, spinal cord, and organs. It is particularly effective in diagnosing conditions such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, and joint abnormalities.
Moreover, MRI can also provide valuable information about blood flow, making it a useful tool in cardiovascular imaging.
In conclusion, while both tomography and MRI serve the purpose of diagnostic imaging, they differ in terms of technology and indications. Tomography, utilizing X-ray technology, provides detailed images of bones and is especially useful for identifying fractures and tumors. On the other hand, MRI, utilizing a strong magnetic field, provides excellent clarity of soft tissues like muscles, tendons, and organs, making it particularly effective in diagnosing brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, and joint abnormalities.
If you are looking for Ressonância magnética: como funciona e quando é indicada - Cirurgião da you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Ressonância magnética: como funciona e quando é indicada - Cirurgião da like Ressonância magnética: como funciona e quando é indicada - Cirurgião da, Tomografia ou Ressonância Magnética: quais as diferenças e indicações? and also Como funciona a ressonância magnética? - Blog OXIMAG. Here you go:
Ressonância Magnética: Como Funciona E Quando é Indicada - Cirurgião Da
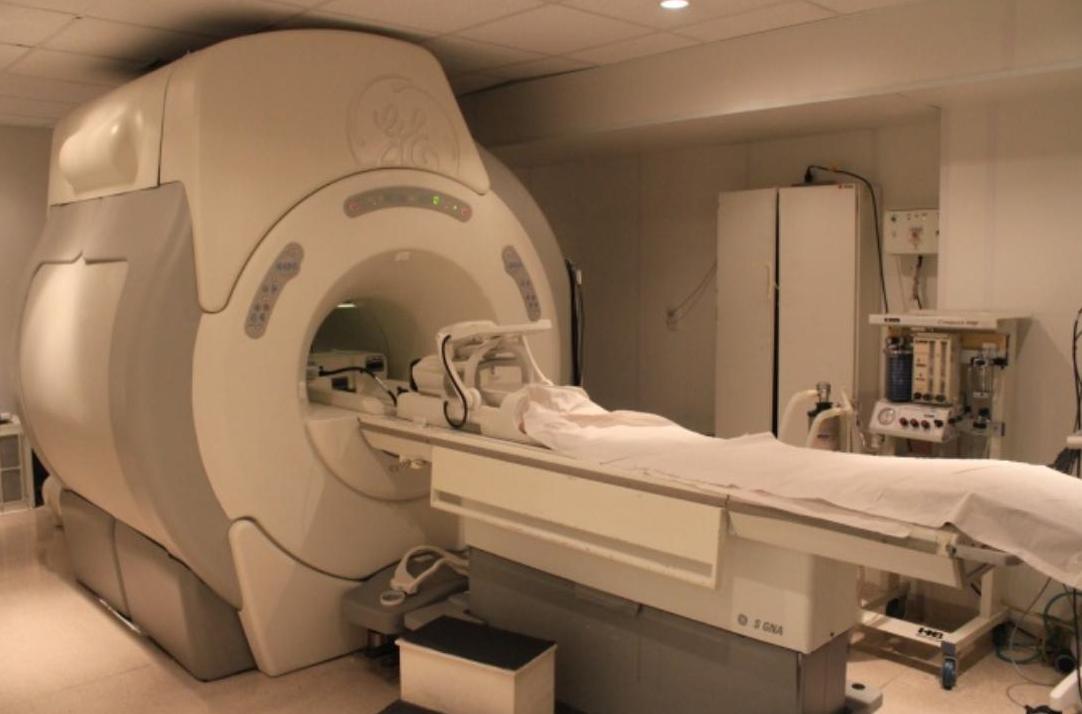
 carloscostamarques.com.brTomografia Ou Ressonância Magnética: Quais As Diferenças E Indicações?
carloscostamarques.com.brTomografia Ou Ressonância Magnética: Quais As Diferenças E Indicações?
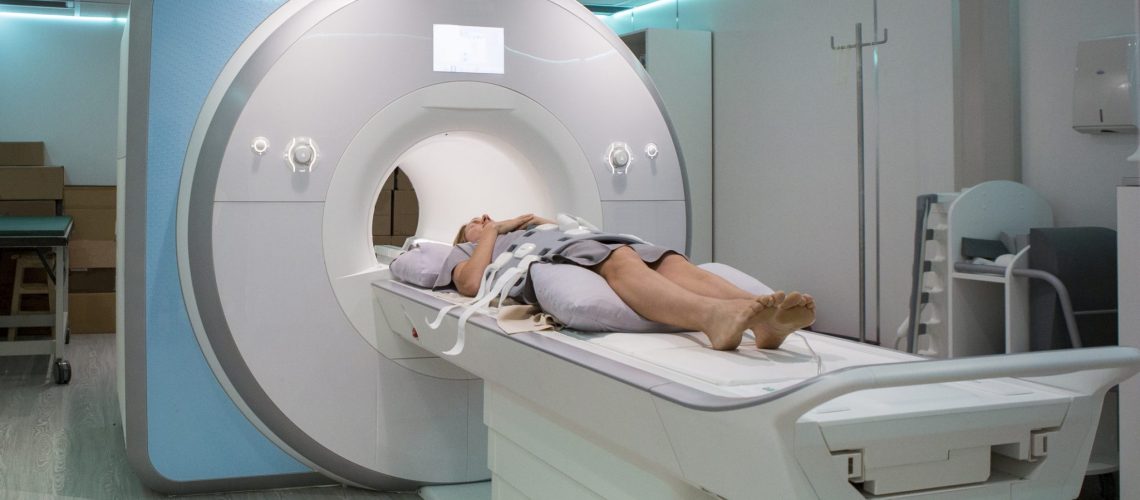
 imeb.com.brComo Funciona A Ressonância Magnética? - Blog OXIMAG
imeb.com.brComo Funciona A Ressonância Magnética? - Blog OXIMAG
 www.oximag.comRessonância Magnética: O Que é E Como é Feito O Exame | Laboratório Exame
www.oximag.comRessonância Magnética: O Que é E Como é Feito O Exame | Laboratório Exame
 laboratorioexame.com.brRessonância Magnética: Tudo O Que Precisa De Saber
laboratorioexame.com.brRessonância Magnética: Tudo O Que Precisa De Saber
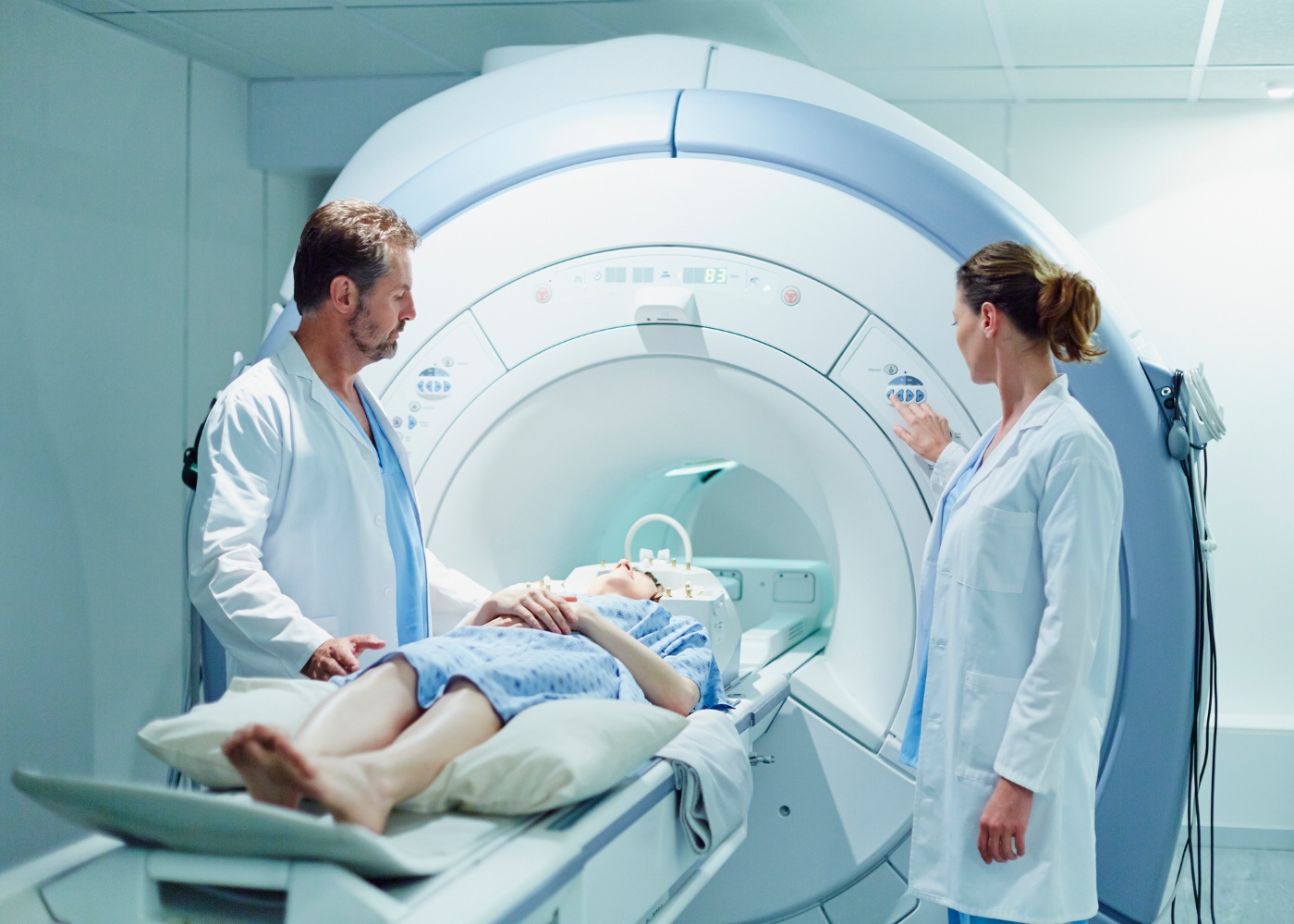 www.e-konomista.ptTomografia ou ressonância magnética: quais as diferenças e indicações?. Ressonância magnética: como funciona e quando é indicada. Ressonância magnética: o que é e como é feito o exame
www.e-konomista.ptTomografia ou ressonância magnética: quais as diferenças e indicações?. Ressonância magnética: como funciona e quando é indicada. Ressonância magnética: o que é e como é feito o exame